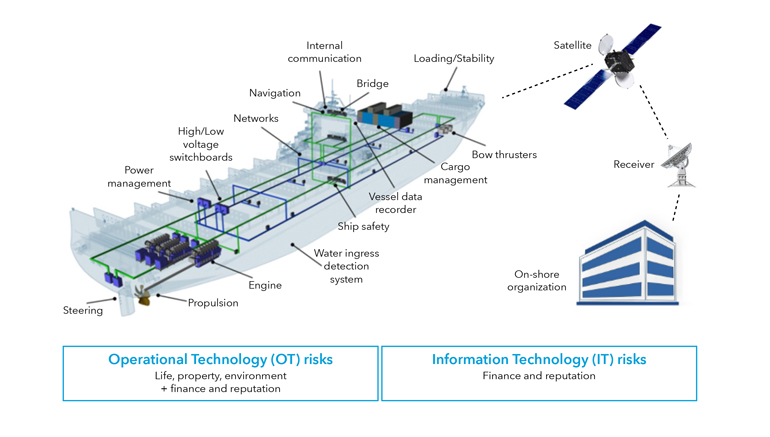
Testing vessel cyber vulnerabilities
Armed with this maritime expertise, DNV’s certified ethical hackers begin with passive and active reconnaissance of a ship’s cyber security. They then scan for potential vulnerabilities. If they find any, they try to gain access through penetration testing.
Testing could start simply by walking around a vessel seeking unauthorized access to a computer server cabinet; because it is unlocked, for example. Access-control related information such as passwords may not be kept securely, and the ethical hackers might try tapping into the crew WiFi to find doors into OT control systems. The ethical hackers would then scan for vulnerabilities that could potentially be used to enter and exploit the system to affect operations or access confidential information (Table 1).
Some of the testing can be conducted remotely using the Internet from DNV’s centres of expertise. “Customers frequently need testing and solutions to be completed within very tight schedules during a vessel’s port visit,” observed Mate Csorba, Manager Security Architecture & Verification, DNV.
Commonly found maritime cyber vulnerabilities
DNV’s maritime cyber security specialists regularly find instances of passwords never being changed or being pre-set by IT departments onshore and printed and posted on walls. Some passwords are weak or just factory defaults.
Sometimes, crew members back up data on personal hard disk-drives, or uncontrolled USB sticks are used to transfer loading-condition data to shore. Infected maintenance laptops connected across different systems are another vulnerability. Then there was the firewall mounted in an engine performance monitoring cabinet, but not connected; the onboard firewall with base functions disconnected; and control system devices connected to insecure onboard IT networks.
Keeping software patched and hardened against cyber-attacks sounds obvious. “But we have seen Windows operating system software being updated only during major upgrades, so it is years out of date. Sometimes Windows is installed with standard settings left unchanged,” said Csorba.
Applying standards in ethical hacking
Ethical hacking needs performing in ways that give shipowners, insurers, and other maritime stakeholders the comfort that internationally recognized standards, guidelines, and best practice are being followed.
For example, DNV Recommended Practice (RP) DNV-RP-0496 for managing the cyber security resilience of ships and mobile offshore units in operation outlines a strategy to assess weaknesses in technology, processes, and people (Figure 2) and provides a scheme on how to prioritize different safeguards.
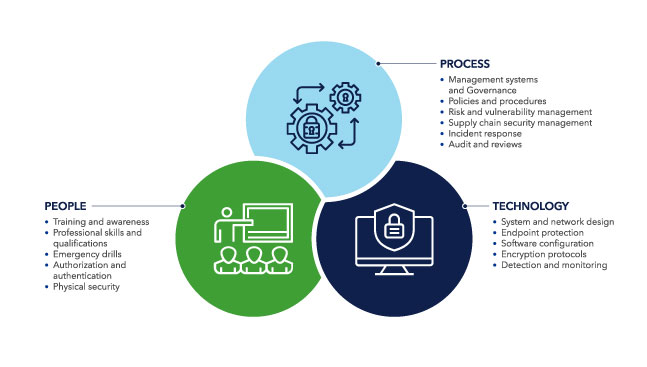
Figure 2: Assessing cyber security in technology, processes, and people
Expecting the unexpected
To have the best defences ready to counter threats, ethical hackers need a large range of hacking tools and deep understanding of the relevant OT and IT systems.
They can draw, for example, on huge, publicly available online databases of vulnerabilities identified worldwide and updated daily, and on industry-standard search tools. That said, they are always aware that threats that have never been encountered before, ‘zero-day vulnerabilities’, can occur.
“You start with the network topology of the integrated OT/IT system and the accompanying asset inventory of hardware and any software running on it, but then don’t know what vulnerabilities you will encounter,” said Csorba. A network topology depicts how a ship’s components interconnect and communicate. Maritime cyber experts such as DNV can also assist in developing network topologies for vessels.
Ensuring cyber secure newbuild and operating vessels
With the huge investment tied up in today’s newbuild vessels, and in the cargos some carry, cyber security rises up the agenda as cyber risk increases and related regulations and de facto regulation (e.g. international standards and guidelines) become more prevalent and stricter.
“We see ethical hacking as a necessary third-party verification step for any critical cyber-enabled infrastructure including vessels,” said Csorba. “By addressing cyber security right from the concept phase, third-party penetration testing activity can be used to validate the effectiveness of the barriers that were initially designed into the integrated system.”
Accurate cyber risk assessment across the maritime value chain is needed to ensure that cyber vulnerabilities in third-party hardware and software are not introduced into vessels. Such assessment is also required to write adequate cyber security requirements into contracts with suppliers and subcontractors.
Ethical hacking can be part of the process leading towards the awarding of DNV class notation Cyber Secure which proves requirements and verification of technical barriers, processes and people awareness based on management of cyber risks on board DNV classed vessels.
Learn more about DNV's maritime cyber security services and solutions
References and further resources:
1 ‘NotPetya offers industry-wide lessons, says Maersk’s tech chief’, W Ashford, computerweekly.com, [online] 7 January 2019
2 ‘Vessel Cyber Risk Management Work Instruction’, US Coast Guard, 27 Oct 2020 ‘MSC-FAL.1/Circ.3
3 ‘Guidelines on maritime cyber risk management’, International Maritime Organization, applicable to in-service vessels since the 1 Jan 2021
4 ‘The Guidelines on Cyber Security Onboard Ships: Version 4’, produced by maritime stakeholder organizations, www.ics-shipping.org, 2021
5 ‘IACS adopts new requirements on cyber safety’, International Association of Classification Societies https://iacs.org.uk/news/iacs-adopts-new-requirements-on-cyber-safety, April 2022
6 ‘Cybersecurity Guidelines for Ports and Port Facilities: Version 1.0’, International Association of Ports and Harbours, iaphworldports.org, 2021
7 ‘BIMCO Cyber Security Clause 2019’, bimco.org
8 ‘Closing the safety gap in an era of transformation', DNV paper, 2021